Jun 7, 2024
This blog post examines the carbon footprint of ChatGPT, highlighting that each query emits around 4.32 grams of CO2. It discusses the environmental impact of AI models during training and usage phases and suggests strategies to reduce their carbon footprint, emphasizing the need for greener solutions.
With the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence, particularly large language models like ChatGPT, questions about their environmental impact are increasingly pertinent. One common inquiry is: how much CO2 does a single ChatGPT query generate? This blog post aims to provide a clear answer, supported by recent studies and expert estimates.
CO2 Emissions Per Query
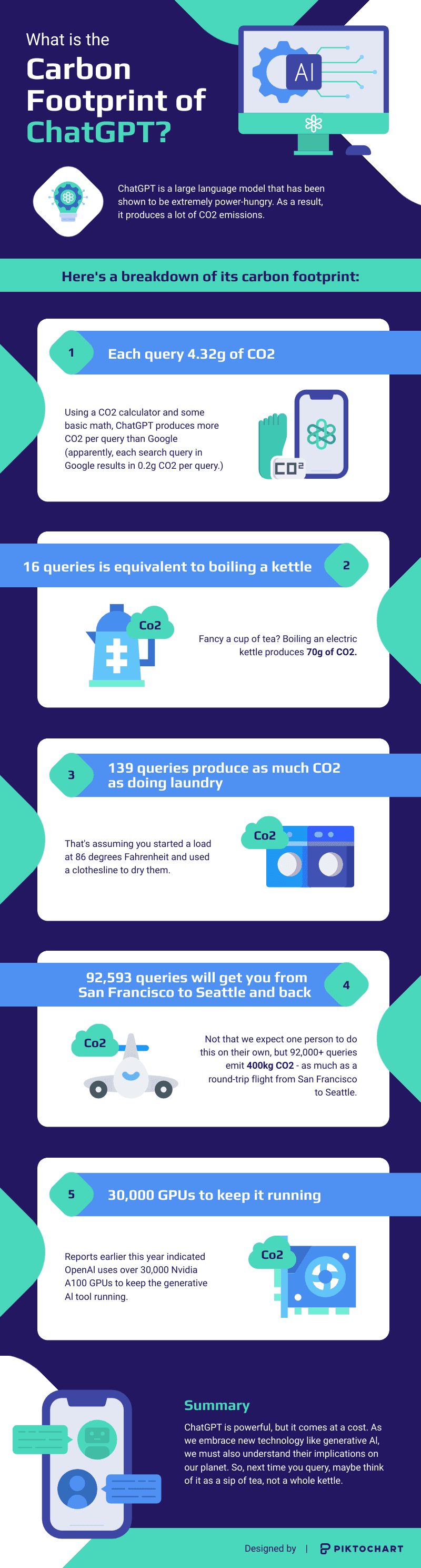
According to various sources, the CO2 emissions of a single query to ChatGPT range between 2.5 to 5 grams. A detailed calculation reveals that each message sent to ChatGPT produces approximately 4.32 grams of CO2. This figure, though seemingly small on an individual level, can accumulate significantly given the volume of queries ChatGPT handles daily (Piktochart) (Sigma Earth).
Breakdown of Environmental Impact
Training Phase: The training of large AI models is resource-intensive. For instance, training GPT-3, which forms the foundation of ChatGPT, consumed around 1,287 MWh of electricity and produced 552 tonnes of CO2, which is equivalent to the emissions from 110 gas-powered cars over a year (Carbon Credits) (karmametrix.com). Training these models involves processing vast datasets over several weeks or months, utilizing thousands of GPUs that consume large amounts of electricity.
Inference Phase: Once the model is trained, the operational phase, known as inference, also consumes substantial energy. Running queries through ChatGPT requires continuous use of computational resources. Industry estimates suggest that each generative AI query uses four to five times more energy than a standard search engine query. While a typical Google search emits about 0.2 grams of CO2, a ChatGPT query can emit up to 1 gram of CO2 (Greenpeace).
Comparing Usage Scenarios
To put these numbers into perspective:
15 ChatGPT queries equate to the CO2 emissions of watching one hour of video streaming.
139 queries are roughly equivalent to the emissions from one load of laundry washed and dried on a clothesline.
For frequent flyers, 92,593 queries would match the carbon footprint of a round-trip flight from San Francisco to Seattle (Piktochart).
Below is an interesting data viz on the topic by Piktochart.
Strategies for Reducing AI’s Carbon Footprint
Greener Data Centers: Utilizing renewable energy sources for data centers can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of AI models. Solar and wind energy are far greener alternatives to coal or gas-fired power plants (Greenpeace).
Efficient Model Design: Implementing more efficient AI model architectures and processors can reduce energy consumption. Studies suggest that improvements in these areas could cut the carbon footprint of AI models by 100 to 1,000 times (Sigma Earth) (Greenpeace).
Sustainable Practices: Scheduling computational tasks during periods when renewable energy is more readily available can further decrease emissions. Additionally, compressing large models and selecting only necessary data for training can also help minimize environmental impact (Sigma Earth).
Conclusion
As AI continues to evolve and integrate into various aspects of life, understanding and mitigating its environmental impact is crucial. The CO2 emissions from a single ChatGPT query might seem minor, but the cumulative effect can be significant given the model's widespread use. Through a combination of greener energy sources, efficient model design, and sustainable practices, the carbon footprint of AI can be managed and reduced.
By being aware of these impacts and striving for more sustainable AI development, we can enjoy the benefits of advanced technology while minimizing harm to our planet.
References
Piktochart. "A Closer Look at The Carbon Footprint of ChatGPT." May 3, 2024. (Piktochart)
CarbonCredits.com. "How Big is the CO2 Footprint of AI Models? ChatGPT's Emissions." May 30, 2023. (Carbon Credits)
KarmaMetrix. "ChatGPT’s Carbon Footprint." February 1, 2023. (karmametrix.com)
Sigma Earth. "The Carbon Footprint of ChatGPT." (Sigma Earth)
Greenpeace. "ChatCO2 – Safeguards Needed For AI’s Climate Risks." (Greenpeace)
By understanding the environmental cost of our digital activities, we can take steps towards more sustainable technology use.

